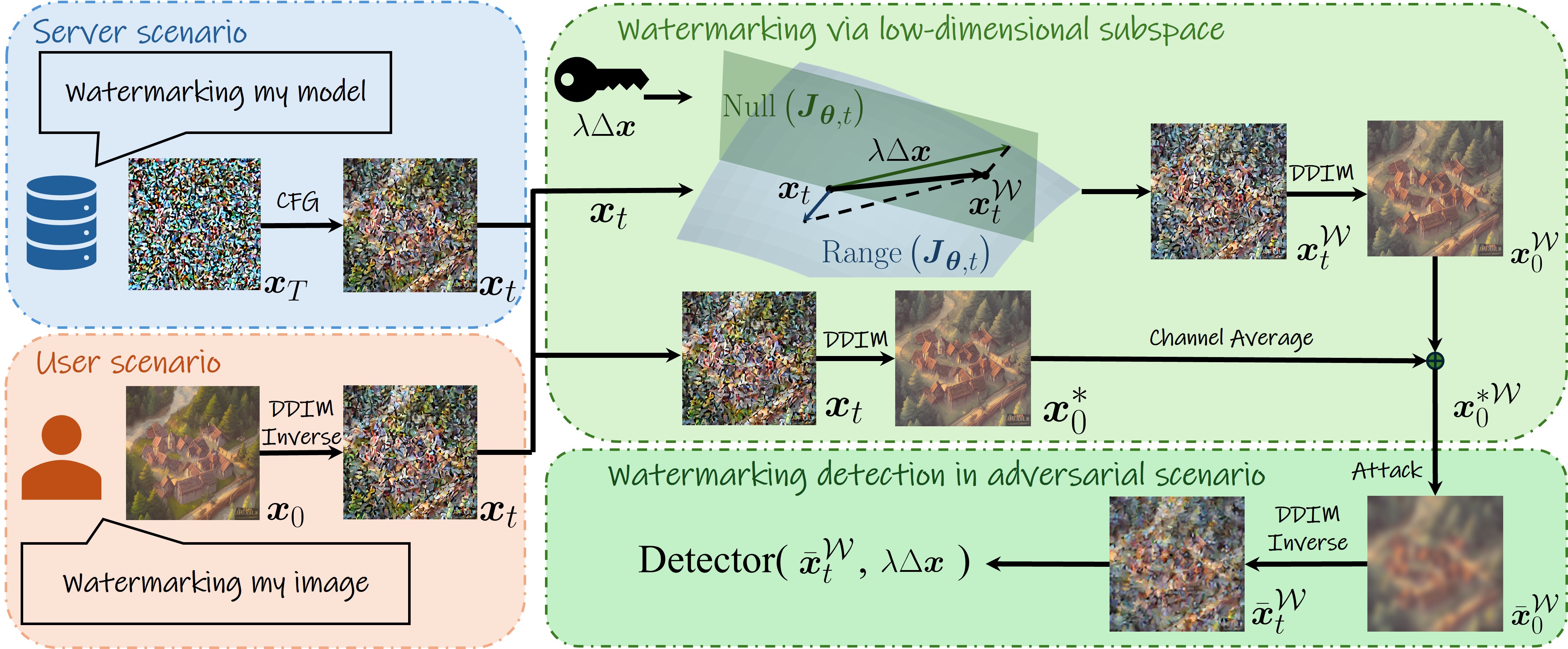
The widespread use of AI-generated content from diffusion models has raised significant concerns regarding misinformation and copyright infringement. Watermarking is a crucial technique for identifying these AI-generated images and preventing their misuse. In this paper, we introduce Shallow Diffuse, a new watermarking technique that embeds robust and invisible watermarks into diffusion model outputs. Unlike existing approaches that integrate watermarking throughout the entire diffusion sampling process, Shallow Diffuse decouples these steps by leveraging the presence of a low-dimensional subspace in the image generation process. This method ensures that a substantial portion of the watermark lies in the null space of this subspace, effectively separating it from the image generation process. Our theoretical and empirical analyses show that this decoupling strategy greatly enhances the consistency of data generation and the detectability of the watermark. Extensive experiments further validate that Shallow Diffuse outperforms existing watermarking methods in terms of consistency.
@inproceedings{
shallowdiffuse,
title={Shallow Diffuse: Robust and Invisible Watermarking through Low-Dim Subspaces in Diffusion Models},
author={Li, Wenda and Zhang, Huijie and Qu, Qing},
booktitle={The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2025},
}